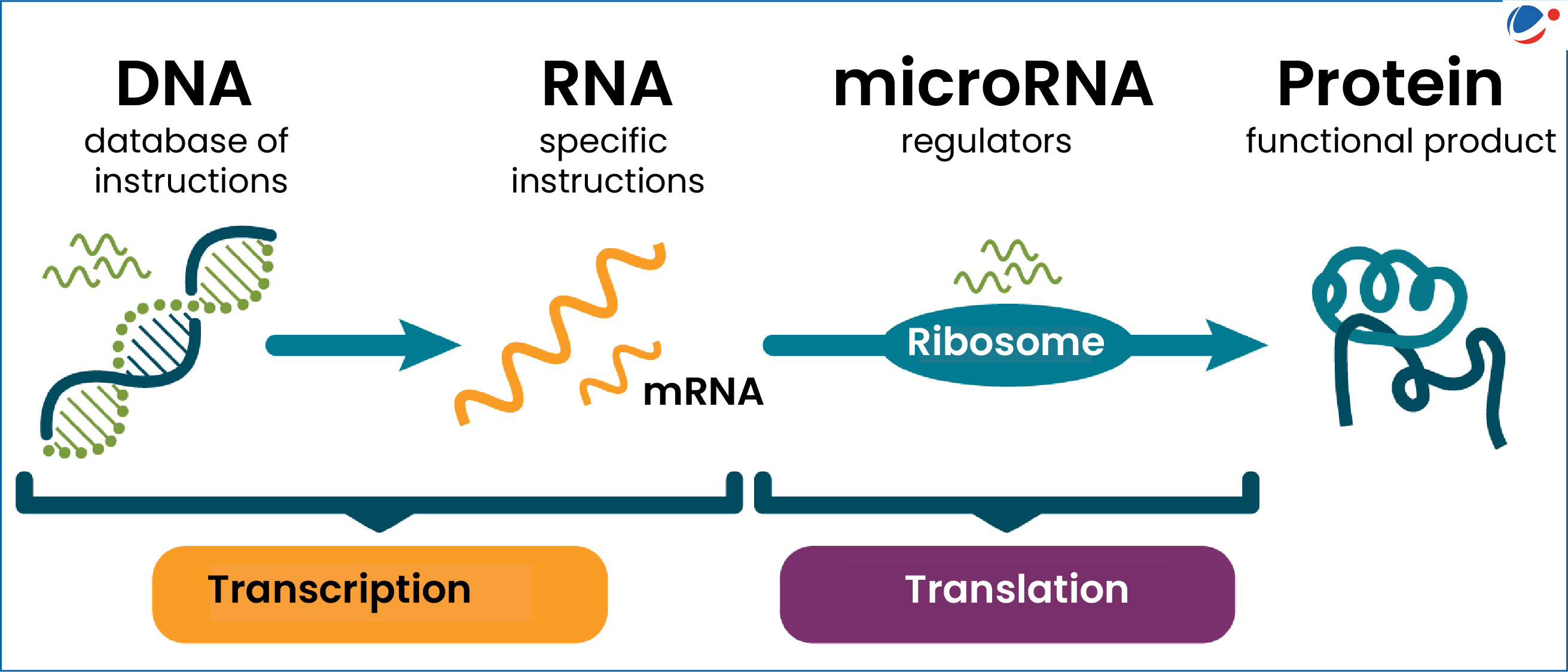
The discovery of microRNA by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the early 1990s revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation, earning them the coveted Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024. Initially met with skepticism, their groundbreaking research revealed that these tiny RNA molecules play a critical role in controlling gene expression across various organisms, including humans. Funded primarily by NIH grants, their work opened the floodgates to a new era of biomedical research, showcasing the profound impact of microRNA on health and disease. As the scientific community began to recognize the significance of these molecular regulators, interest soared, and their implications for RNA therapeutics came to the forefront. Today, the world is witnessing an incredible transformation in medicine, all sparked by the simple yet profound discovery of microRNA.
In the realm of molecular biology, the identification of small non-coding RNAs has emerged as a key milestone, with microRNA standing out for its pivotal role in gene regulation. This category of RNA molecules, initially observed in the model organism C. elegans, has been found to have extensive implications for human health, influencing everything from developmental processes to disease mechanisms. The journey from its initial discovery to contemporary applications demonstrates the potential of these tiny RNAs to reshape therapeutic strategies, particularly in the fight against complex diseases. Fueled by numerous NIH grants, researchers are increasingly focusing on the multifaceted impact of microRNA, paving the way for innovations in RNA-based therapies. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of microRNA, the promise of targeted treatment options becomes increasingly viable, heralding a new era of precision medicine.
The Revolution of microRNA Discovery
In the early 1990s, the discovery of microRNA by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros was a groundbreaking moment that would eventually reshape our understanding of gene regulation. This innovative work, published in *Cell*, detailed the complex role of microRNAs in the gene expression mechanism of the C. elegans roundworm. While the initial reception of their findings didn’t set the scientific community ablaze with enthusiasm, it laid crucial groundwork to explore genetic regulation across various species, including humans. Over the years, this humble discovery garnered increasing attention, eventually leading to transformative advancements in molecular biology.
The impact of microRNA transcendental findings became more apparent as the field of RNA research expanded. Researchers around the globe recognized that these small RNA molecules played a critical role in not just simple organisms but also in plants and humans. This realization triggered a surge of interest in microRNAs and their potential applications in health and disease, resulting in significant NIH grants that fueled extensive research. Consequently, Ruvkun and Ambros’ initial work ignited a revolution within genetic research, suggesting that microRNA is a fundamental building block essential for understanding organismal development and functioning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key discoveries related to microRNA that led to the Nobel Prize for Gary Ruvkun?
The pivotal discoveries in microRNA research made by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the 1990s revealed a new level of gene regulation in C. elegans. This foundational work, which largely went unnoticed initially, ultimately earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine. Their research highlighted the critical role of microRNAs in regulating gene expression across various organisms, laying the groundwork for ongoing studies in RNA therapeutics and gene regulation.
How has research funded by NIH grants advanced the understanding of microRNA?
NIH grants have significantly advanced microRNA research by providing essential funding to scientists like Gary Ruvkun, allowing them to explore and validate the roles of microRNAs in gene regulation. This funding has facilitated breakthroughs that demonstrate the widespread impact of microRNAs, not only in C. elegans but also in higher organisms, including humans, contributing to the development of innovative RNA therapeutics for various diseases.
What is the impact of microRNA on human health and disease?
MicroRNAs play a fundamental role in regulating gene expression, influencing how genes translate into proteins. Research has identified around 1,000 microRNAs in the human genome that control the majority of protein-producing genes, which has direct implications for human health. Currently, therapies based on microRNA research are in clinical trials aimed at treating significant health issues such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s.
What role did Gary Ruvkun play in the discovery of microRNA?
Gary Ruvkun, alongside Victor Ambros, was instrumental in the discovery of microRNA in the early 1990s. Their research focused on how these small RNA molecules regulate gene expression in C. elegans, which was groundbreaking at the time. This work not only laid the foundation for future microRNA studies but also significantly contributed to the field of molecular biology, culminating in their recognition with the 2024 Nobel Prize.
Why is federal funding important for microRNA research and its future?
Federal funding has been crucial for microRNA research, with the majority of Gary Ruvkun’s lab support coming from NIH grants. This financial backing has enabled sustained investigation into microRNA functions and their applications in RNA therapeutics. Advocating for continued federal investment is essential to prevent shifts away from groundbreaking scientific research, which is vital for ongoing discoveries and pharmaceutical advancements.
How are microRNA discoveries influencing RNA therapeutics?
MicroRNA discoveries are significantly influencing the development of RNA therapeutics aimed at treating genetic diseases and various health conditions. Companies specializing in RNA interference therapies, such as Alnylam, have emerged as leaders in the field, demonstrating the potential of microRNAs in innovative treatment solutions. This illustrates the transition from basic research into practical applications that can revolutionize healthcare.
What challenges do researchers face in the microRNA discovery field today?
Researchers in the microRNA discovery field face several challenges, including securing consistent funding and navigating the transitions between basic research and commercial applications. With scientific exploration influenced by public and private funding streams, maintaining a stable environment for innovative research is critical. Additionally, concerns regarding the future career pathways for young scientists in the field highlight the need for ongoing support and investment in RNA research.
What advancements have been made in RNA therapeutics as a result of microRNA studies?
Advancements in RNA therapeutics stemming from microRNA studies include the development of targeted therapies that leverage microRNA’s ability to regulate gene expression. These innovations are currently in clinical trials for conditions like heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders, showcasing the potential of microRNA research to transform treatment paradigms and improve patient outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, publishing their findings in the journal Cell in 1993. |
| Initial Reception | Their discovery was initially not well-received; it took years for the broader scientific community to recognize its significance. |
| Evolution of Interest | Over time, interest in microRNA grew, particularly as its importance became evident across various species. |
| Impact on Science | MicroRNAs play a critical role in gene regulation affecting development and diseases. |
| Funding Importance | The research was primarily funded through NIH grants, emphasizing the value of government support in scientific advancements. |
| Clinical Applications | MicroRNA-based therapies are being developed for various diseases, including cancer and Alzheimer’s. |
| Career Concerns | Ruvkun expressed concerns about the future of scientific careers due to potential funding cuts. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery has significantly transformed our understanding of genetics and cellular processes. The groundbreaking work of Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the early 1990s laid the foundation for a field that is now pivotal in genetics research and biotechnology. As therapies based on microRNAs move into clinical trials, their impact on the treatment of various diseases underscores the ongoing importance of nurturing scientific inquiry through funding and support.